Recently, the new paper "3D3M: 3D Modulated Morphable Model for Monocular Face Reconstruction" jointly published by Minivision Technology and Nanjing University of Technology was accepted by the top international journal IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (TMM).
TMM Journal is sponsored by the IEEE Computer Association and is an authoritative journal in the field of computer image and video processing worldwide. It belongs to the SCI Zone 1 journal.
This paper proposes a modulated 3D deformable model (3D3M) for monocular 3D facial reconstruction. This model can achieve more detailed and realistic 3D facial reconstruction effects based on a single image.
It is worth mentioning that this has provided us with new innovative inspiration in facial reconstruction technology. In the future, this technological achievement can also be widely applied in fields such as virtual makeup, facial special effects, and facial stylization.

Question raising
The goal of 3D facial reconstruction is to extract information such as facial identity, expression, texture, lighting, posture, etc. from the image, and reconstruct the shape and material of the face.
As an important technology in multimedia applications, 3D facial reconstruction from a single image is quite challenging, as the difficulty lies in the reconstruction ambiguity caused by the lack of depth information.
Currently, most existing methods rely on annotations or strong prior information fitted by traditional methods. In contrast, we propose a novel modulated 3D deformation model (3D3M) that learns dense shape correspondence from monocular images in a self supervised manner.
Technical Proposal
The overall framework of the model is divided into two parts: sparse shape response and dense shape response.
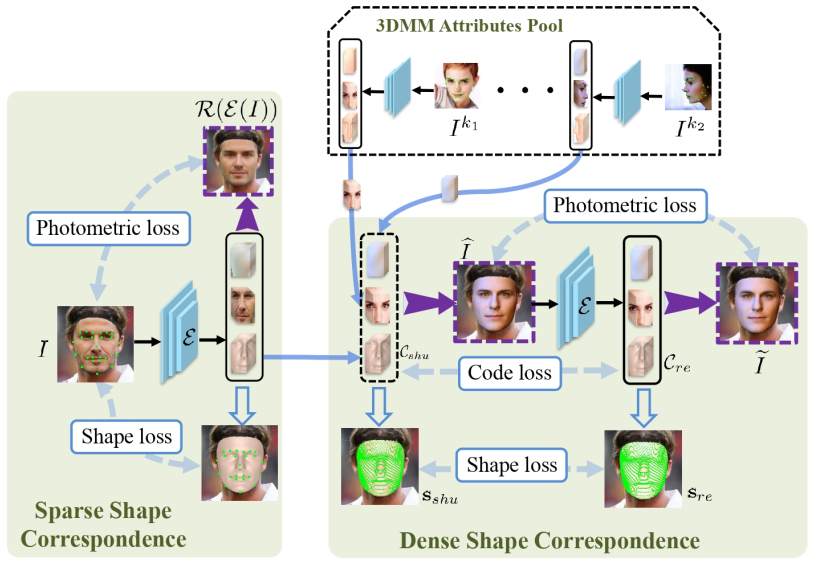
In the first part, we use cyclic consistency constraints to reconstruct sparse key points and pixels of the image and input image.
In the second part, given a batch of input facial images, 3D3M will encode their facial attributes (id, expression, texture, lighting, etc.), and then randomly recombine the features to generate a new facial image. The recombined features are rendered using a differentiable renderer, which enables us to use dense shape correspondence and reconstructed pixel consistency for self supervised learning.
Two parts can be trained end-to-end. Both quantitative and qualitative experimental results have demonstrated that 3D3M can construct realistic and high-quality 3D facial reconstruction effects from monocular images, outperforming existing technologies in 3D facial reconstruction and alignment tasks.
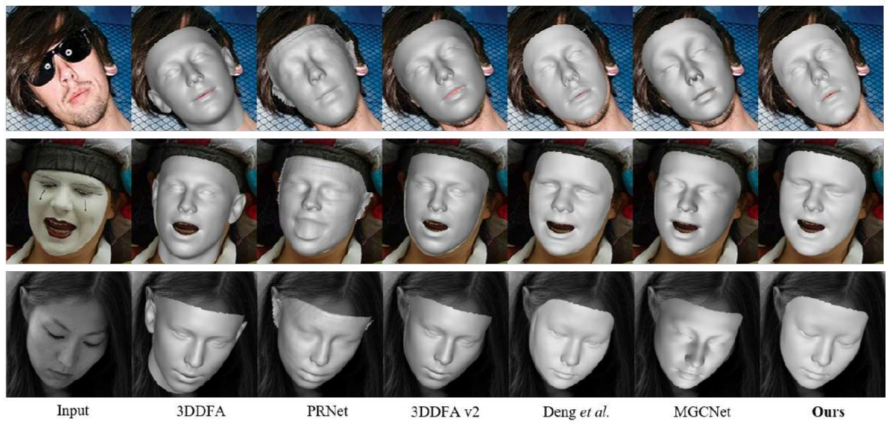
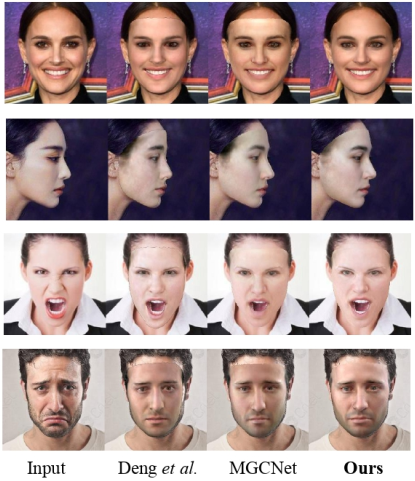
Effect comparison

We compared the best existing models on the MICC Florence, BU-3DFE, and AFLW2000-3D datasets, and found that the accuracy of the 3D3M model reached the SOTA level.
From the perspective of reconstruction effect, the 3D3M model can provide precise shapes, fitting textures, and delicate expressions, and has good robustness against side faces and occlusion.


Conclusion and Outlook
As an important foundational capability for multimedia applications, 3D facial reconstruction has shown enormous potential for application. Compared to traditional sparse key points, fine modeling of faces can provide unprecedented richness in detail. In addition, with the popularity of short videos and video calls, the importance of basic algorithms on mobile devices is gradually becoming prominent.
On the basis of the algorithm theory proposed in this paper, Minivision AI Research Institute combines strategies such as knowledge distillation to create a lightweight facial reconstruction model, which can achieve real-time reconstruction on the mobile end with equal accuracy, providing over 30000 ultra precise and dense key points to meet the needs of various video special effects.
With the increasingly widespread application of AR, VR, metaverse, and other related fields, 3D vision has become a cutting-edge and popular research direction in the field of artificial intelligence, which contains enormous commercial value and has a promising future. With the accumulated technology, Minivision AI Research Institute will continue to explore research fields such as large-scale scenes and universal 3D object reconstruction in the future.














